Welcome to the third part of my blog series. In this blog series, I’ll give you a tour through the features that Microsoft Endpoint Manager offers us. In the last two blogs, we looked at the topics of device and application management. Today we would like to take a look at device security. The biggest goal companies have is to protect their devices and data from outsiders. Every day there are new attack methods or threats that companies need to protect against. MEM provides many features that use the power of the cloud to achieve this goal. At the center of this is Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
More blogs from this series:
- Part 1 – Devices
- Part 2 – Applications
- Part 3 – Endpoint Security – this blog
- Part 4 – Reports
- Part 5 – User and Groups
Where can I find the security features in MEM Portal?
These features can be found in the Endpoint Security menu on the left side of the MEM portal. At the center of this is Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
When you open this menu, you will land on an Overview page. Here you will get tips for the first steps and a short explanation of what Endpoint Security is. The description from Microsoft is as follows:
Enable, configure, and deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to help prevent security breaches and gain visibility into your organization’s security posture.

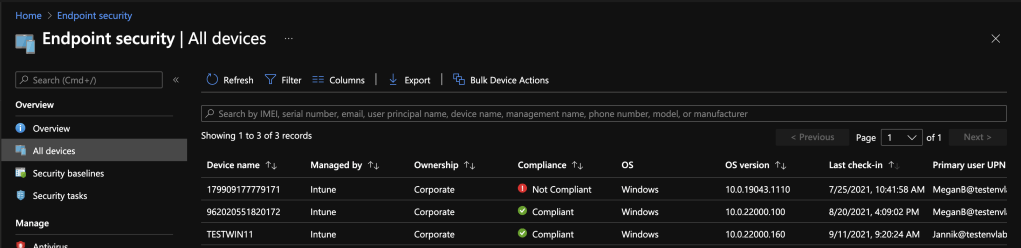
All devices
A similar menu is already familiar to us from the previous blogs. Here you get an overview of all devices and their security status. You can see the compliance state of the devices, which OS build they are running and when the last check-in to Intune was.
Security baselines
Security baseline are predefined security settings to make the start into a modern management with Windows 10 easier and secure. These policies were created by security experts from the industry. These baselines are updated by Microsoft with each release of a new Windows version. You can still customize the predefined settings when you create them.

Security tasks
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint can be used to scan the entire environment for current threats. If a security event is detected in the Microsoft Defender Security Center that needs to be fixed in MDM, a security colleague can create a task to have an MDM colleague look at it. When the task is done, it can also be marked as done.

Antivirus
In this section you have on the one hand several reports and on the other hand you can create antivirus policies. On the home page you can see the health status of the endpoints and a count of active malware.
With the “Unhealthy endpoints” report you get a list of clients where the security status is not given, e.g.
Signature update overdue. In the “Active malware” report you get a list of active malware in your company.
You also have the possibility to distribute antivirus configurations for server operating systems. These must be integrated into the ConfigMan.
There are 4 types of policies that can be created:
- Microsoft Defender Antivirus exclusions (Windows 10)
- Windows Defender Antivirus (Windows 10)
- Windows Security experience (Windows 10)
- Antivirus (macOS)

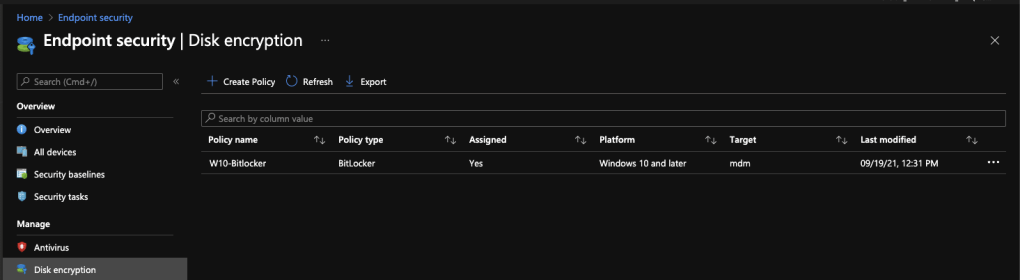
Disk encryption
In this section you can configure Bitlocker on Windows or FileVault on Mac. Disk Encryption helps you protect your data on the device in case the device is lost or stolen.
Here you can configure the security as well as the usability of both services. The encryption keys are backed up in the MEM.
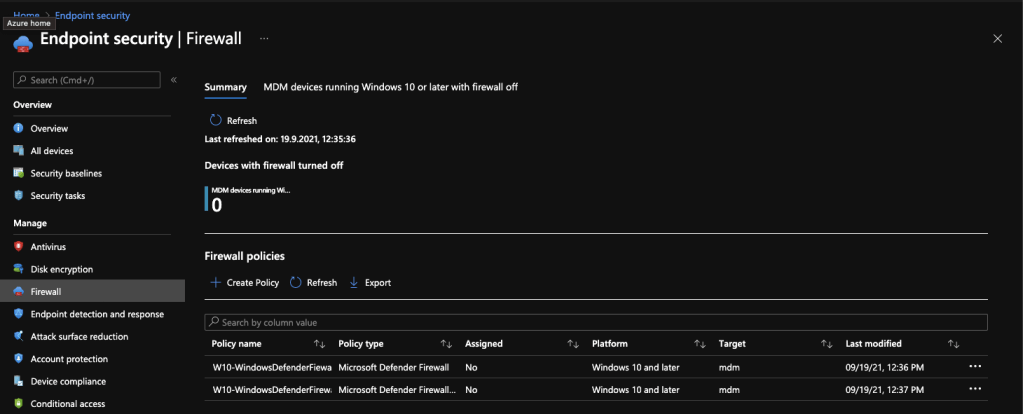
Firewall
ere you have 2 types of configuration. You can configure the general behavior of the firewall via “Microsoft Defender Firewall” and you can allow or block individual connections via “Microsoft Defender Firewall rules”.
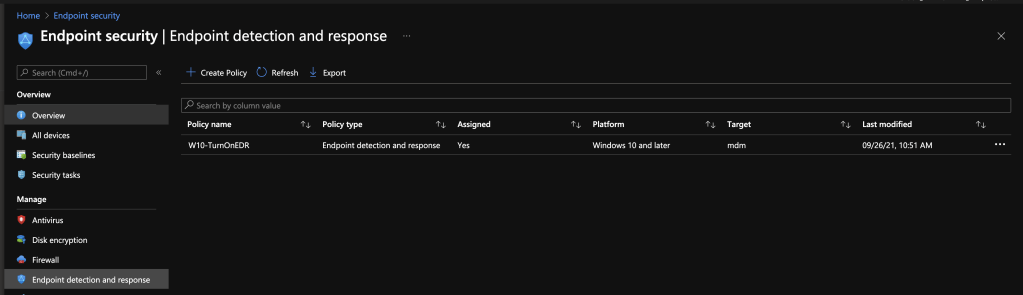
Endpoint detection and response
This feature provides advanced attack detection by collect cyber telemetry data that is applied in near real time. This data is retained for up to 6 months and provides analysts with the ability to go back to specific times when an attack occurred. This data can also be used for forensic capabilities. Here the options “Sample sharing for all files” and “Expedite telemetry reporting frequency” can be configured.
Attack surface reduction
ASR policies are mitigation options for known attack surfaces. As of today, there are 6 different types of policies that can be created.

Device control
Here you can configure how to handle external devices. For example, entire Bluetooth devices can be deactivated.
Attack surface reduction rules
Here the creation of subprocesses for some tools can be blocked or the behavior of script executions can be adjusted or blocked completely.
App and browser isolation
The Application Guard can be activated here. This function allows to execute browser session in a temporary sandbox, thus preventing access to the host system.
Exploit protection
Here you can upload an XML with a set of exploit protection. This can be applied to individual apps or to the OS. How you can create this XML is explained here.
Web protection
With this function, you can enable the Microsoft Defender web content filter or, for example, block the download of unverified files. You can also activate SmartScreen, which has a blacklist of malicious urls that you must confirm before accessing the page.
Application controll
Here you can configure the App locker application control. With Applocker you can e.g. block only the execution of certain software. You can also configure the Windows SmartScreen here.
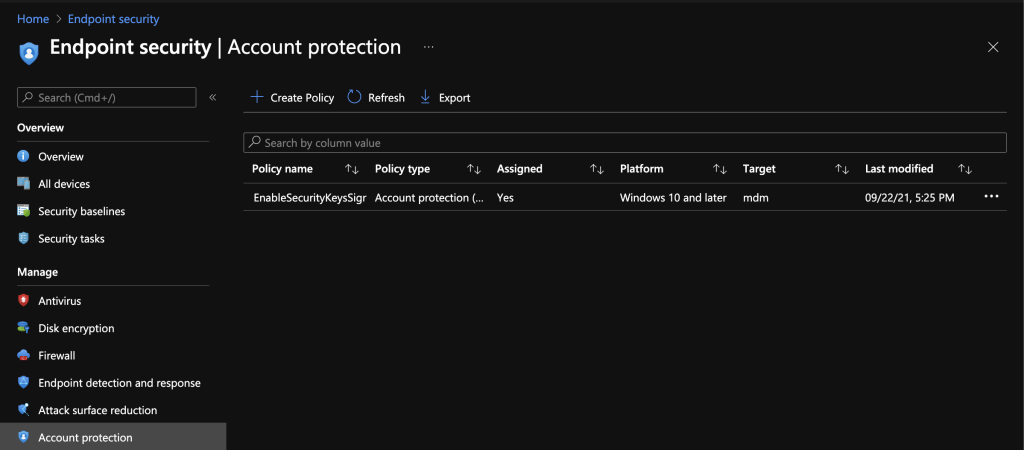
Account protection
This feature is a preview feature. Here is a second place where you can configure Windows Hello for Business. The login with security keys and the credential guard can also be activated in this menu. Windows Defender Credential Guard can be used to additionally secure credentials under Windows 10 and protect them from attacks. In this option
Device compliance
Compliance Policy can ensure the security of devices and the protection of corporate data. With the help of this policy, devices can be marked as compliant or not compliant. These are rules that define what a device must comply with, such as Bitlocker encryption, a minimum OS version, etc.
This device status can be used for conditional access.

There are the following submenus for the compliance policies area:
Policies
- Define new compliance policies and an overview of existing ones. Here you can also see which policies are assigned and which are not.
Notifications
- Here you can define mail notifications if a device is not compliant. Mail templates can be created in different languages.
Retire Noncompliant Devices
- Decommissioning devices after they have been non-compliant for some time. This action removes the device from Intune management and removes all corporate data from the device.
Locations
- In this menu, locations can be defined based on network information.
Compliance policy settings
- Further options for compliance policies can be found here like the default state if no policy is defined, an enhanced jailbreak detection can be enabled and the days of the compliance status validity period can be defined.
Conditional access
Access policies are definitions/instructions that a user or device must meet in order to access certain resources. For example, if you need to access certain data, a pre requisite may be that your device must be complaint.
A other example: if a user is outside the company network a multi factor authentication is required.
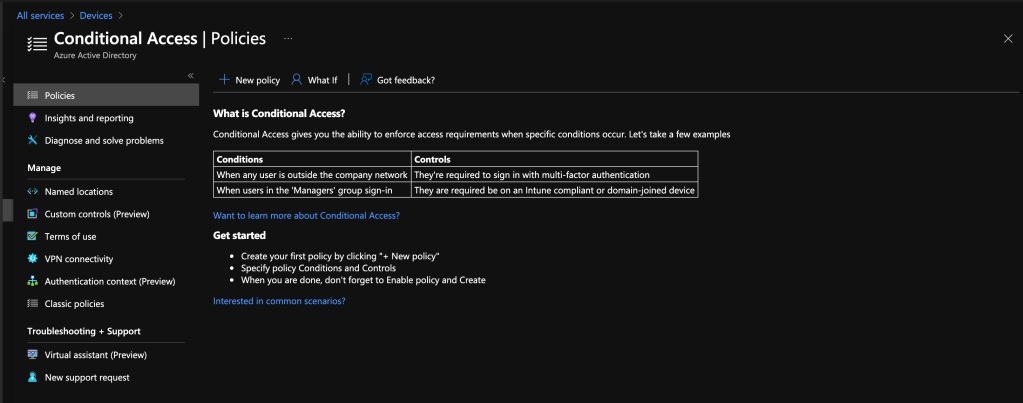
Policies
- In this section the Conditional Access policies can be defined. There is the possibility to create policies as report only to get only an overview or to activate the policies actively. How to configure a Conditional Access is explained very well in the blog of peter van der woude.
Insights and reporting
- Here CA data can be sent to an Azure Log Analytics Workspace to get an advanced reporting dashboard.
Diagnose and solve problems
- Help and troubleshooting instructions.
Named locations
- Here, trusted locations / company networks can be defined on the basis of IP information. This data can then be used for CA policies.
Custom controls (Preview)
- Custom CA controls can be defined here based on a JSON. To satisfy this control, a user’s browser is redirected to the external service, performs the required authentication, and is then redirected back to Azure Active Directory. Azure Active Directory checks the response, and if the user is successfully authenticated or validated, the user continues with the conditional access flow.
Terms of use
- Here the terms of use can be defined in different languages. If the terms of use are defined and enforced via CA, a page opens where you have to accept them.
VPN connectivity
- In this option, a certificate for an always on VPN connection can be created. More information about the alway on VPN with CA can be found here.
Authentication context (Preview)
- With authentication context, applications can trigger policy enforcement when a user accesses sensitive data or actions. How to configure this you can find here.
Classic policies
- Tool for migration of old CA policies not created in Azure portal to new framework.
Virtual assistant (Preview)
- Chatbot for Azure Active Directory Topics.
New support request
- Wizard to open Azure Active Directory tickets or get existing solutions.
Assignment failures
Policies for which the assignment failed are displayed here. This can be a security risk if certain policies do not take effect on devices.

Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
In this menu you can enable Windows Defender Advance Threat Protection and connect it to Intune. Additionally you have here the possibility to provide the machine risk score for compliance policies. You will also find a reporting on how many devices defender is installed on.

Help and support
This menu can be found in several places in the MEM portal. Here you have the possibility to get help, to open tickets or to access already opened tickets.
In the last year, Microsoft has seen a 40% growth in sales in the security sector. Microsoft also invests over one million euros in this area every year. This can also be seen in Intune. There are also countless features to increase the security in your company. Here we can also expect many new features in the future.
Thank you very much for reading this blog. If you like this blog I would be very happy about a like or a share.
We hear us in the next part of this series.
Until then:
Stay healthy, Cheers
Jannik


[…] Part 3 – Endpoint Security […]
LikeLike
[…] Part 3 – Endpoint Security […]
LikeLike
[…] Part 3 – Endpoint Security […]
LikeLike
[…] Part 3 – Endpoint Security […]
LikeLike